 |
THE PROCESS OF GASIFICATION:
Promising Technology for Energy and Environmental Sustainability
Gasification is a process that converts carbonaceous materials such as biomass, coal and minucipal waster into gases such as H2, CO, CO2, CH4, H2O, N2 through a series of chemical reactions. Other byproducts of gasification are hydrocarbons and higher boiling pyrolysis products (tar) and a solid residue (biochar). The thermochemical process occurs in a gasifier, a high-temperature and high-pressure vessel that uses oxygen or air and steam to directly contact the feed material. The resulting gases, known as syngas, can be used as a fuel for power generation, heating, and transportation, or as a feedstock for the production of chemicals and other materials.
One of the major advantages of gasification technology is its ability to use a wide range of feedstocks, including waste materials that would otherwise end up in landfills. This not only reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills but also provides a sustainable source of energy. Another advantage is the high efficiency of the process that extracts more energy from the same amount of feedstock, reducing the overall cost of energy production. Furthermore, gasification produces fewer emissions than traditional combustion processes, making it a cleaner and more environmentally friendly technology.
Gasification technology has many applications in various sectors. In the power generation sector, gasification can be used to produce electricity by using syngas to fuel gas turbines or by converting syngas to steam for use in a steam turbine. Gasification can also be used in the transportation sector by producing biofuels such as synthetic diesel and ethanol. In the chemical industry, syngas can be used as a feedstock for the production of chemicals such as methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen.
SYNGAS GENERATION
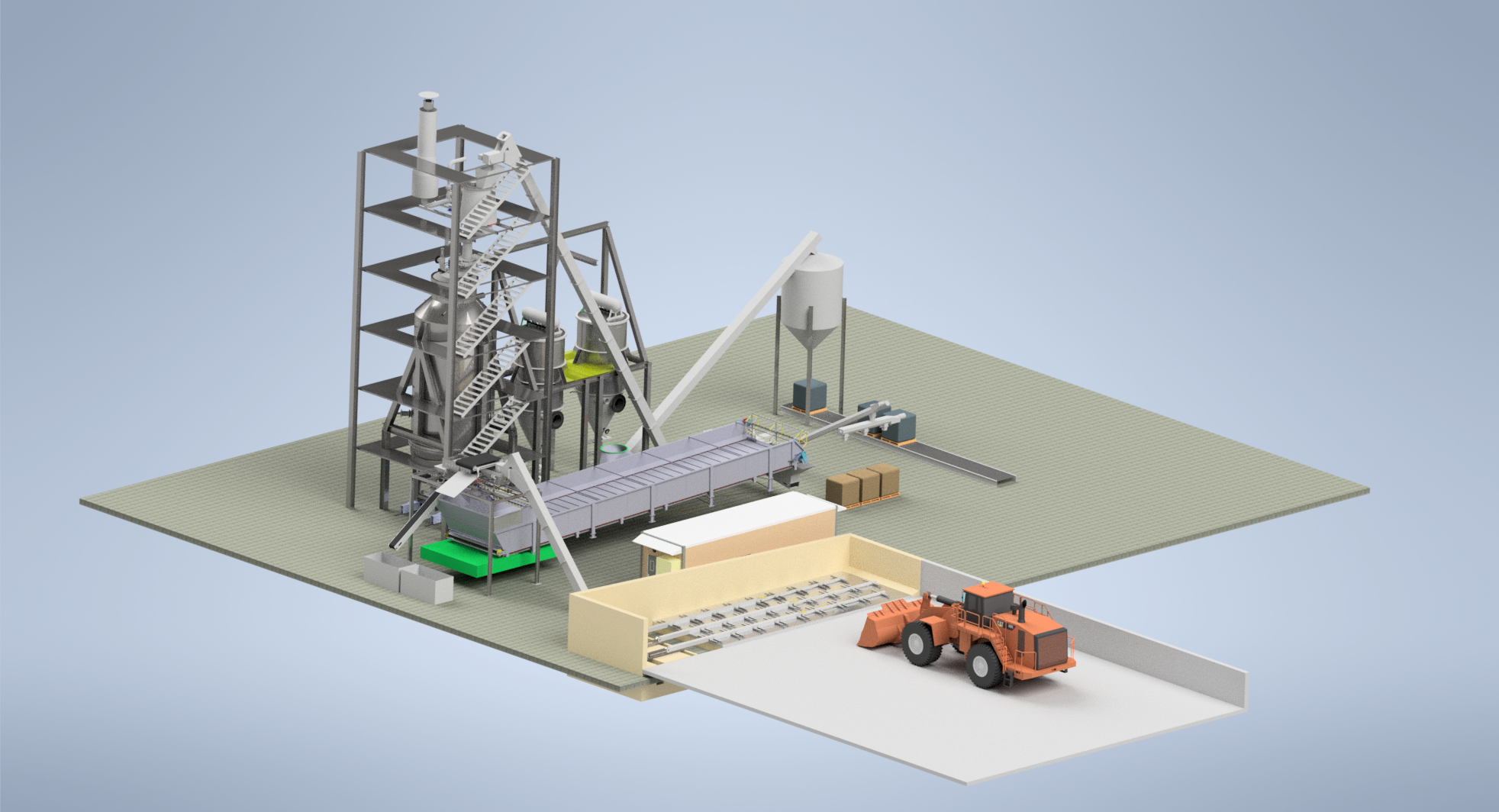 |
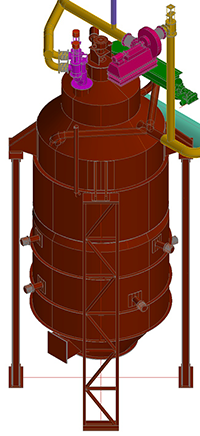
The patented and patent pending Biomass Gasification Technology uses woodchips and other biomass for high quality, tar free, syngas generation.
The gasification reactor utilizes novel three stage, integrated Pyrolysis, POX Gasification and Reduction processes in single vessel at high temperatures and high conversion and thermal efficiency. Pyrolysis process temperatures are in the 600°C range and POX gasification process operates at 1,100°C. The generated syngas is cooled and filtered prior to being used in internal combustion (IC) engines.
Syngas generation byproducts are clean ash (biochar), steam and heat, all of which have commercial use.